Clinical Manifestations
• Fatigue, IUGR, preterm deliv, perinatal mortality, pica, restless leg syn
• Hb <6 g/dL a/w NRFHT, oligohydramnios, fetal death, CHF (Hb <4 g/dL)
• Signs: Pallor (conjunctiva), tachy, orthostatic HoTN, jaundice (hemolysis), splenomegaly (thal, sickle cell, spherocytosis), petechiae (TTP, HUS, DIC)
Diagnostic Evaluation
• CBC w/ indices at 1st OB visit & 24–28 w gest; note MCV, RDW, retic count
• Periph smear, iron, iron sat, ferritin, TIBC, folate, B12, Hb electrophoresis
• Additional labs: LFTs, BUN/Cr, TFTs, hemolysis labs (↑ indirect bili, ↑ LDH, ↓ haptoglobin)
• Bone marrow aspirate/bx
• RI = [retic count × (pt’s Hct/nml Hct)]/maturation factor
Figure 16.1 Initial approach to anemia
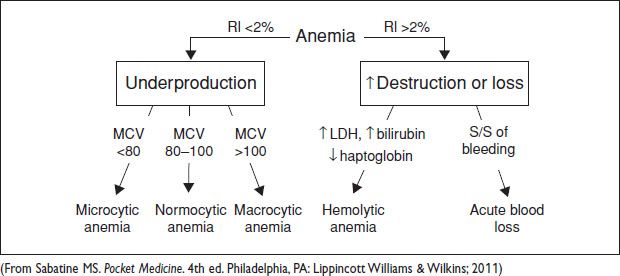
Maturation factor dependent on Hct; Hct ≤15% = 2.5, >16% = 2, >26% = 1.5, >36% = 1 (Nml is 1–2% for healthy  . >2–3% = adequate retic for anemia. <2% = inadeq.)
. >2–3% = adequate retic for anemia. <2% = inadeq.)
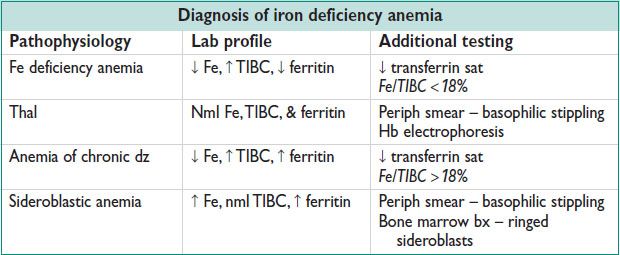
Microcytic Anemia (MCV <80 fL)
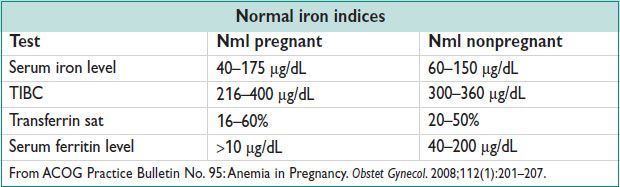
• Eval: Serum Fe, TIBC (transferrin), ferritin, transferrin sat
• 30 mg/d of elemental iron req during Preg for prevention of anemia
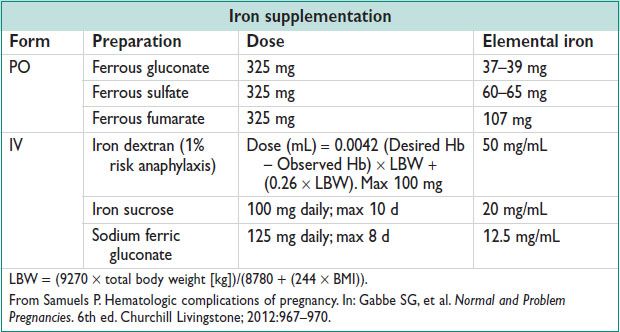
• Rx: Fe rich foods (cream of wheat, red meat, spinach, dried beans; take w/ Vit C rich foods for ↑ Absorp), Fe supplements, IV iron (intolerance to PO), xfusion (for symptomatic anemia or Hb <6), erythropoietin
Normocytic Anemia (MCV 80–100 fL)
• DDx includes acute bld loss, early Fe deficiency, bone marrow suppression (marrow invasion, RBC aplasia, aplastic anemia), chronic renal insufficiency, hypothyroidism, pancytopenia, anemia of chronic dz, sideroblastic anemia
Macrocytic Anemia (MCV > 100 fL)
• Megaloblastic anemia: Hypersegmented neutrophils on periph smear is pathognomonic
Folate deficiency: Age, malnut (alcoholism), malabsorption (celiac sprue), meds (trimethoprim, methotrexate), ↑ requirement (Preg, malig, dialysis)
B12 deficiency: May cause neurologic sx; causes – pernicious anemia, gastritis, bariatric Surg, malabsorption (Crohn’s, ileal resxn, tapeworm), meds (metformin, PPIs)
• Nonmegaloblastic anemia: Causes include liver dz, alcoholism, reticulocytosis, hypothyroidism, myelodysplastic syn, medication (AZT, acyclovir, azathioprine)
• Eval: Serum B12/folate, periph bld smear, homocysteine, methylmalonic acid
↑ homocysteine in B12 & folate deficiency, ↓ methylmalonic acid in B12 deficiency only
Schilling test, anti-IF antibodies → positive in pernicious anemia
• Rx: Folate deficiency – 1–5 mg PO QD → will treat anemia but, not neuro sx; B12 deficiency – 1 mg IM QD × q7d then weekly × 4 w then monthly as needed
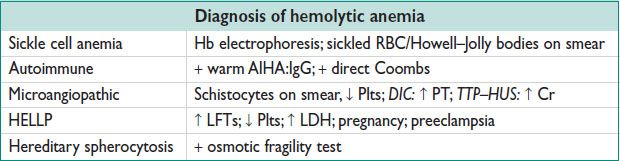
Hemolytic Anemia
• Eval: ↑ retic count (RI >2%), ↑ LDH, ↓ haptoglobin, ↑ indirect bilirubin
• Direct Coombs test, periph smear, Hb electrophoresis, osmotic fragility test
HEMOGLOBINOPATHIES
Pathophysiology
• Adult Hb structure = 2 α-chains + 2 β-chains (HbA) or 2 δ-chains (HbA2)
• Fetal Hb = 2 α-chains + 2 γ-chains (HbF) (12–24 w gest)
Thalassemias (Lancet 2012; 379:373)
• Abn or ↓ synthesis of α- or β-chains → microcytic anemia; classified by absent chain
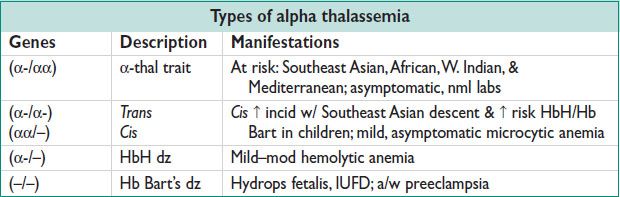
• a-thal: 4 α-chains (αα/αα) from 2 genes on chromo 16
Absence of ≥1 of 4 genes → abn Hb assembly → hemolysis & ↓ production
• b-thal: Nml state = 2 β-chains from 1 gene on chromo 11
At risk: Mediterranean, Asian, Middle Eastern, Hispanic, & West Indian
1 β-chain mut → β-thal minor → mild anemia
2 β-chain mutations → β-thal major (Cooley’s anemia) → sev anemia
β-thal intermedia = 2 β-chain mutations w/ milder sx
• Dx: CBC (MCV < 70), ferritin (exclude Fe deficiency anemia), Hb electrophoresis, periph smear → basophilic stippling
• Screening in Preg: Pts in high-risk groups → CBC & Fe indices → ↓ MCV & no iron deficiency → Hb electrophoresis; If Southeast Asian, DNA testing for α-thal
• Prenatal testing for α- & β-thal if mut/deletions in both parents via CVS, amnio, or PGD
• Preg in β-thal major recommended only if nml cardiac fxn & prolonged hypertransfusion → Hb >10 & w/ iron chelation
• Rx: xfusion for anemia + iron chelation; splenectomy; hematopoietic xplant
Sickle Cell Anemia (Lancet 2010;376:2018; Obstet Gynecol 2007;109(1):229)
• Autosomal recessive β-chain mut (valine replaces glutamic acid at 6th amino acid) resulting in abn Hb structure (HbS replaces HbA)
• HbS (heterozygote) = sickle cell trait (carrier); HbSS (homozygote) = sickle cell anemia
• HgbSS: ↓ oxygen tension → RBC sickles → hemolysis & microvascular occlusion
• 1 in 12 AAs w/ trait, 1 in 500 w/ dz; ↑ risk African, Mediterranean, Arab-Indian
• Signs/sx:
Anemia hemolysis, splenic sequestration, aplastic (parvovirus B19)
Infarction: Painful crises, acute chest syn, CVA, multiorgan failure: Functional asplenia, kidneys (renal papillary necrosis), heart, & brain (CVA)
Infxn encapsulated organisms (Hib, S. pneumoniae, Meningococcus), osteomyelitis
• Acute chest syn = new pulm infiltrate + a pulm symptom (chest pain, T > 38.5, resp sx, hypoxemia) from infxn/vaso-occlusion of pulm vessels; 3% mortality
• Dx: bld smear w/ sickle-shaped RBCs & Howell Jolly bodies; Hb electrophoresis
• Rx: hydroxyurea → ↑ HbF → ↓ frequency of painful episodes, acute chest syn & need for bld xfusion; bld xfusion → simple vs. exchange xfusion (indications: Preop, acute/chronic organ failure, acute anemia, acute pain); iron chelation; hematopoietic stem cell xplant (selected pts w/ sev dz)
Acute pain crisis → Opioids are mainstay, O2 for oximetry <95%, IV hydration
Infxn → vaccination against Hib, S. pneumoniae, N. meningitidis, influenza, & HBV
Acute chest syn/CVA → simple vs. exchange xfusion (ACS = respiratory symptoms, chest pain, or fever and a new pulmonary infiltrate on XR)
• Sickle cell variants: HbC not a/w dz, HbSC same as HbSS but ↓ frequency; HbS + thal a/w varying severity of dz
• Preg: HbSS a/w ↑ mat risk acute pain crises, acute chest syn, PROM, preeclampsia, pyelo, bld xfusion, alloimmunization, & infxn; ↑ fetal/neonat risk SAB (30%), IUFD (OR = 2), IUGR, PTD (25%), ↓ birth weight (20–40%). Prenatal diagnosis available
Mgmt: Stop hydroxyurea (teratogenic), start 1–4 mg folate daily, avoid cold, physical exertion, dehyd, & stress to avoid painful crises. If xfusion → monit serial Hb & % HbS, goal: Hb ∼10 g/dL & ≤40% HbS (Obstet Gynecol 2007;109(1):229)
Serial growth USs & antenatal testing at 32 w for fetal monitoring
HbSS & HbS (trait) w/ ↑ risk of pyelo w/ asymptomatic bacteriuria. Consider daily UTI ppx & monthly urine cx.
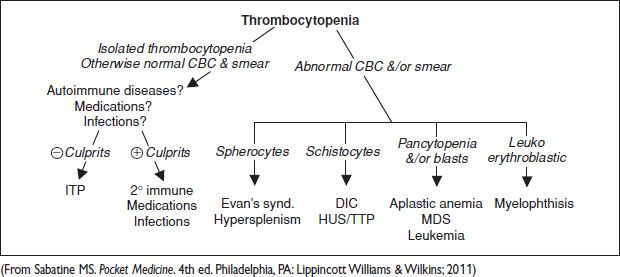
THROMBOCYTOPENIA (PLT <150000/μL)
• Plt 50000–100000 – no increased surgical risk; ↑ risk for bleeding w/ major trauma
• Plt 20000–50000 – ↑ risk w/ minor trauma or Surg
• Plt <20000 – risk spont bleeding (<10000 ↑ risk of life-threatening bleeding)
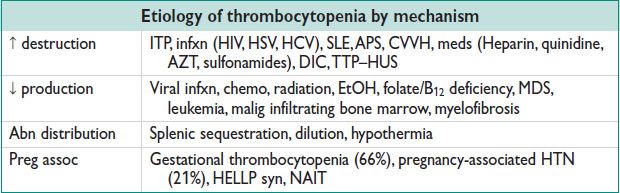
Etiology
• Gestational thrombocytopenia → 8% of pregnancies; most common cause of ↓ Plt in Preg (66%); Plt typically >70000/μL; resolves 2–12 w postpartum
• ITP → IgG-mediated; persistent Plt <100000/μL; dx of exclusion (nml bld smear, no systemic dz); 15% of neonates have Plt <50000/μL if MoM has ITP (trans placental IgG).
• HIT → see Section below
• TTP–HUS → thrombocytopenia + microangiopathic hemolytic anemia ± renal failure ± fever ± Δ mental status; etiology: Meds (quinine, chemo, cyclosporine), Preg, Shiga toxin-producing E. coli, SLE, sev ADAMTS13 deficiency
• DIC → etiology: Sepsis, Preg (abruption, HELLP, PPH, IUFD, septic AB, preeclampsia), Surg, hepatic failure, xfusion rxn
NAIT → mech similar to RhD dz; 1st Preg can be affected; ∼0.1% live births; risk of IVH, petechiae, bleeding; ∼100% recurrence for future pregnancies if fetus has same Plt Ag
• HELLP syn → see Chap. 15.
Evaluation
• H&P: PMHx, meds, infxns, splenomegaly, LAD, petechiae, mucosal bleeding
• Labs: CBC ± periph smear; retic count, LDH, haptoglobin, bilirubin, PT/aPTT, fibrinogen, D-dimer, Coombs, ANA, enzyme-immunoassay for HIT, HIV, HCV, Parvovirus, CMV, antiphospholipid antibodies, bone marrow bx
Figure 16.2 Initial approach to thrombocytopenia