Chapter 311 Congenital Anomalies
311.1 Esophageal Atresia and Tracheoesophageal Fistula
Seema Khan and Susan R. Orenstein
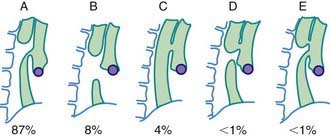
Esophageal atresia (EA) is the most common congenital anomaly of the esophagus, affecting ∼1/4,000 neonates. Of these, >90% have an associated tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF). In the most common form of EA, the upper esophagus ends in a blind pouch and the TEF is connected to the distal esophagus. The types of EA and TEF and their relative frequencies are shown in Figure 311-1. The exact cause is still unknown; associated features include advanced maternal age, European ethnicity, obesity, low socioeconomic status, and tobacco smoking. This defect has survival rates of >90%, owing largely to improved neonatal intensive care, earlier recognition, and appropriate intervention. Infants weighing <1,500 g at birth have the highest risk for mortality. Fifty percent of infants are nonsyndromic without other anomalies, and the rest have associated anomalies, most often associated with the VATER or VACTERL (vertebral, anorectal, [cardiac], tracheal, esophageal, renal, radial, [limb]) syndrome. These syndromes generally are associated with normal intelligence. Despite low concordance among twins and the low incidence of familial cases, genetic factors have a role in the pathogenesis of TEF in some patients as suggested by discrete mutations in syndromic cases: Feingold syndrome (N-MYC), CHARGE syndrome (coloboma of the eye, central nervous system anomalies; heart defects; atresia of the choanae; retardation of growth and/or development; genital and/or urinary defects [hypogonadism]; ear anomalies and/or deafness) (CHD7), and anophthalmia-esophageal-genital syndrome (SOX2).