CHAPTER 1 amount of acoustic energy the patient receives. as low as reasonably achievable; used to reduce biological effects in humans and the fetus. interaction of the sound wave with microscopic gas bubbles found in tissues. study of the human body at work. describes the likelihood of cavitation occurring. Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA) an act passed by Congress to assure safe and healthful working conditions. average intensity throughout the pulse duration. force exerted by the sound beam on an absorber or reflector. average intensity across the entire sound beam. peak intensity found across the sound beam. average intensity during the pulse repetition period. greatest intensity during the pulse. relates to the heating of tissue. relates to the heating of bone. thermal index for cranium (TIC) relates to the heating of the cranium. thermal index for soft tissue (TIS) relates to the heating in soft tissue. Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders (WRMSD) • Act passed by Congress in 1970 to assure safe and healthful working conditions. • An agency of the U.S. Department of Labor. • Covers employers and their employees either directly through federal OSHA or through an OSHA-approved state program. • Assures safe and healthful working conditions for workers by setting and enforcing standards and providing training, outreach, education, and assistance. 2. Result in days away from work. 3. Involve musculoskeletal disorder symptoms that remain for 7 days or more. 4. Involve musculoskeletal disorder symptoms that require medical treatment beyond first aid. • Include injuries of the muscles, tendons, and joints. • Greater than 80 percent of sonographers have some form of WRMSD, most commonly shoulder pain. Types of Musculoskeletal Injuries • Position examination table at a proper height with the patient close enough to avoid bending and reaching. • Place monitor directly in front of operator, positioning the monitor height so eyes are even with the top of the monitor. • Ergonomic chair positioned for proper back alignment and foot support to avoid twisting and reaching. • Keep elbow close to body with shoulder abduction at an angle ≤30 degrees. • Maintain neutral hand position. • Avoid resting wrist on the keyboard. • Wear properly fitting glove to maintain a loose grip on the transducer (avoid pinch grip). • Never place transducer cord around the neck. • Neutral position of neck to avoid bending or twisting. • Avoid static work posture; alternate between standing and sitting positions. • Use of ergonomic support cushions. • Position ultrasound system close to body. • Regular stretching and strengthening exercises. • Knowledge of bioeffects is important for the safe and prudent use of ultrasound. • The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates ultrasound instruments according to application, output intensities, and thermal and mechanical indexes. • The American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine (AIUM) recommends prudent use of ultrasound in the clinical environment by minimizing exposure time and output power. • As Low As Reasonably Achievable (ALARA). • Achieve information with the least amount of energy exposure to the patient. • Use of high receiver gain and low output power. • Power should be decreased in obstetric and pediatric examinations. • Exposure time should be kept to a minimum. • Benefit must outweigh risks. • Intensity varies across the sound beam. • Intensity is highest in the center of the sound beam and falls off near the periphery. • Intensity varies with time and is zero between pulses. • Intensity varies within a pulse, starting high and decreasing near the end of the pulse. • Lowest- to highest-intensity values for various imaging modalities include: • 1–200 mW/cm2 spatial peak–temporal average (SPTA) for gray-scale imaging. • 70–130 mW/cm2 SPTA for M-mode imaging. • 20–290 mW/cm2 SPTA for pulsed-wave Doppler. • Intensity of pulsed-wave Doppler is greater than continuous-wave Doppler.
Clinical safety
Occupational safety and health act (OSHA)
Work-related musculoskeletal disorders (WRMSD)
Types of injuries
TYPE
DESCRIPTION
CAUSE
Bursitis
Inflammation of a joint bursa, commonly the shoulder
Repetitive motion
Repeated arm abduction restricts blood flow to the soft tissues
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Entrapment of the median nerve as it runs through the carpal bones of the wrist
Repeated flexion and extension of the wrist Mechanical pressure against the wrist
Cubital tunnel syndrome
Entrapment of the ulnar nerve as it runs through the elbow
Repeated twisting of the forearm
Mechanical pressure against the elbow as it rests on the examination table
de Quervain’s disease
Specific type of tendonitis of the thumb
Repeated gripping of the transducer
Epicondylitis
Inflammation of the periosteum area of the insertion of the biceps tendon into the distal humerus
Repeated twisting of the forearm
Rotator cuff injury
Fraying or tearing of the rotator cuff of the shoulder
Repeated arm abduction
Repetitive motion
Spinal degeneration
Intervertebral disk degeneration
Awkward postures
Static posture
Tendonitis
Inflammation of the tendon and the sheath around the tendon
Repetitive motion
Repeated arm abduction
Thoracic outlet syndrome
Nerve entrapment that can occur at different levels
Repetitive motion
Awkward postures
Trigger finger
Inflammation and swelling of the tendon sheath in a finger entraps the tendon and restricts the motion of the finger
Repeated gripping of the transducer
Prevention of injury
Bioeffects and ALARA principle
Safety
ALARA principle
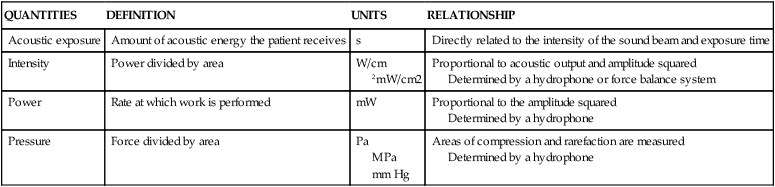
QUANTITIES
DEFINITION
UNITS
RELATIONSHIP
Acoustic exposure
Amount of acoustic energy the patient receives
s
Directly related to the intensity of the sound beam and exposure time
Intensity
Power divided by area
W/cm
2mW/cm2
Proportional to acoustic output and amplitude squared
Determined by a hydrophone or force balance system
Power
Rate at which work is performed
mW
Proportional to the amplitude squared
Determined by a hydrophone
Pressure
Force divided by area
Pa
MPa
mm Hg
Areas of compression and rarefaction are measured
Determined by a hydrophone
Intensity of ultrasound
Clinical safety



