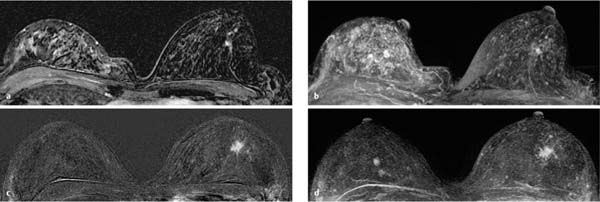
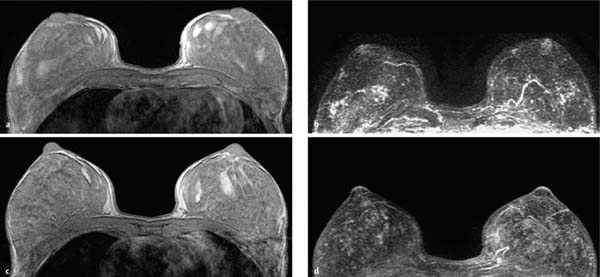
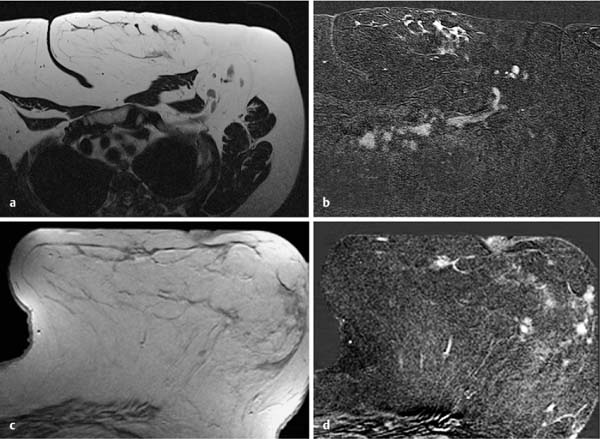
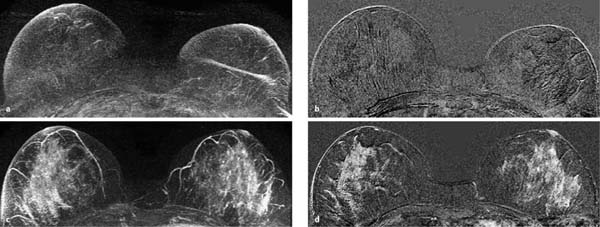
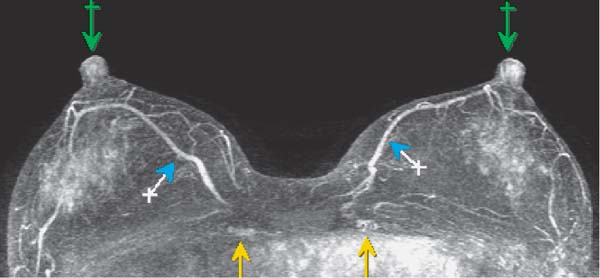
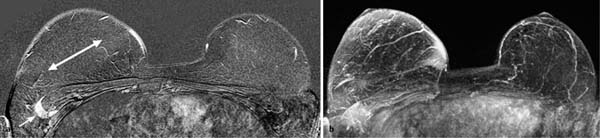
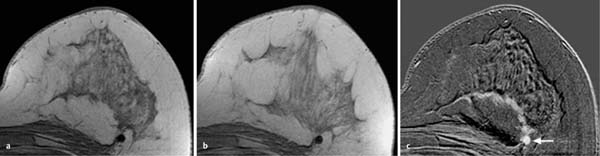
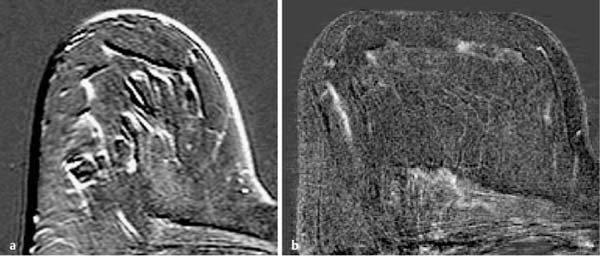
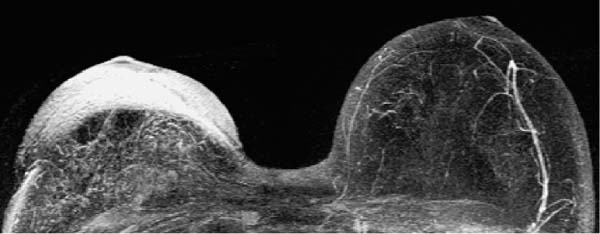
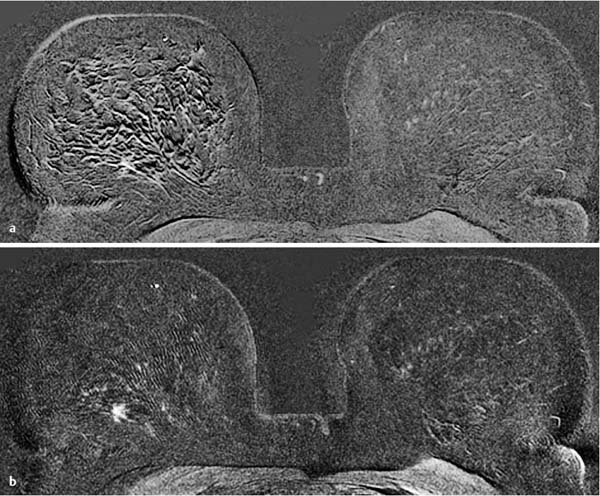
6 Artifacts and Sources of Error The patient to be examined is typically placed in the prone position. Ideally, the breasts are examined in a hanging position in an open breast coil. It is important to take care that all areas of the breast hang freely and completely in the coil lumen and not outside its sensitive volume. The complete imaging of the breast within the breast coil lumen can be verified before beginning dynamic measurements. The T2w sequence performed before the dynamic examination is well suited for this purpose and can easily be repeated if inadequate positioning must be corrected (Figs. 6.1, 6.2, 6.3). Fig. 6.1a–d Inadequate breast positioning—lateral displacement. a Subtraction slice image. Incorrect positioning of the breast inside the surface coil with bulging of breast tissue on the left side of both breasts. b MIP of subtraction images (external examination). c Repeat examination with correct positioning of the breasts and better depiction of several fibroadenomas in the right breast, and a radial scar in the left breast. d MIP of subtraction images. Fig. 6.2a–d Inadequate breast positioning – nipple. a T1w precontrast slice image. Incorrect positioning of the nipple (not imaged hanging free and in ventral position). b MIP of subtraction images with false impression of retromamillary enhancement. c Repeat examination with correct positioning of the nipples. d MIP of subtraction images now shows nipples in profile. Fig. 6.3a–d Inadequate breast positioning—use of body coil in supine body position. a External breast MRI examination performed using a body coil in supine position because of large breast size (T1w image). b Corresponding subtraction image with unusual depiction of thoracic and mammary structures. c Repeat examination with correct positioning of the breasts using a dedicated open breast coil. d Corresponding subtraction image with familiar depiction of mammary structures. Perivenous injection of contrast medium. The perivenous injection of contrast medium (CM) can remain undetected if only the precontrast and subtraction images are evaluated. Subtraction images, in particular, will simulate normal findings in this case. Occasionally, white ribbonlike zones due to motion artifacts can be mistaken for contrasting veins (Fig. 6.4). To ensure the correct intravasal administration of contrast, therefore, it is necessary to detect a definite enhancement in typical reference points (e.g., intramammary veins, internal mammary arteries, Fig. 6.5). If the complete contrast dose has been injected perivenously, the breast MRI examination can be repeated as soon as the source of error has been rectified. Inadequate NaCl flushing. The failure to inject a sufficient volume of normal saline after contrast administration results in ~4 mL of contrast material not being administered because it remains in the extension tubing. This leads to a significant underdosage of CM. For a woman with a body weight of 70 kg and a desired dosage of 0.1 mmol Gd-DTPA/kg body weight, this volume results in a 30% reduction of the effective dose. Since this has an effect on the signal enhancement, it may result in misinterpretation of the results. These examinations should be repeated after an interval of at least 12 hours. Fig. 6.4a–d Failed administration of contrast. a MIP of subtraction images. b Representative subtraction slice image shows slight motion artifacts without definite indications of correct contrast administration. c Repeat examination after reconnection of IV tubing (MIP image). d Representative subtraction slice image of repeat examination. Fig. 6.5 Reference points for verification of correct contrast administration. • Contrasted internal mammary arteries (yellow arrows). • Nipple enhancement (green arrows). • Contrasted intramammary veins (blue arrows). Motion artifacts seen in MR mammography have two major causes. One is the transmission of heart pulsations, which predominantly affects the left breast of slender patients. The other main cause is movement by the patient during the examination (Figs. 6.6, 6.7). Performing breast MRI with an open breast coil and a special compression device to assure adequate breast compression (see Chapter 3) reduces the degree of motion artifacts significantly (Fig. 6.8). Fig. 6.6a, b Motion artifacts due to relaxation of pectoral muscle during dynamic examination. a Subtraction image. Motion due to relaxation of pectoral muscle results in an artifact band at the lateral end of the right pectoral muscle (arrow), as well as white and black motion artifacts at respectively the medial and lateral skin boundaries (double-headed arrow). b MIP. Fig. 6.7a–c Motion artifact mimicking masslike abnormality. a T1w precontrast image. Clip artifact near pectoral muscle. b T1w postcontrast image. Movement of the pectoral muscle results in a relative displacement of the clip. c Subtraction image. Ribbonlike zones with signal loss (black) or signal summation (white) result from movement. False-positive “mass” results from displacement of the clip artifact (arrow) in image subtraction. Fig. 6.8a, b Motion artifact due to not using breast compression device. a Subtraction image with unacceptable motion artifacts (MRI artifact level III). External examination was performed without using an appropriate breast compression device. Interpretation yielded a nonmasslike lesion. b Repeat examination with adequate breast compression (MRI artifact level I). Normal findings. Subtraction images. The quality of subtraction images is especially sensitive to motion artifacts during the dynamic measurements. The effect is generally seen as the presence of black-andwhite ribbonlike zones lacking image information. Such artifacts are occasionally seen to a lesser degree in the peripheral areas of the affected breast. They also occur within the breast parenchyma, however, and are most often seen near the pectoral muscle due to thoracic breathing movements (Fig. 6.7a). False-negative and false-positive findings. Even minor motion artifacts can mask relevant breast findings. In particular the presence of a nonmasslike lesion can then easily be missed (Fig. 6.10). On the other hand, motion artifacts can produce areas that look like a lesion but are not (a false-positive, Fig. 6.11). The degree of motion artifacts should be assessed and documented in the written report of each breast MRI examination. This helps indicate how informative this specific examination is and the relative possibility that a pathological lesion could be missed. In this context, a 4-level classification system equivalent to the x-ray mammograpy ACR breast composition patterns has proven itself useful (Table 6.1). Breast MRI examinations with no motion artifacts (MRI artifact level I) consequently have optimal sensitivity for the detection of breast cancer. Breast MRI examinations with an unacceptable level of motion artifacts (MRI artifact level IV), on the other hand, are not suitable for the early detection of breast cancer (Fig. 6.12). Fig. 6.9 “Snow-peak” effect—motion artifacts in MIP presentation of subtraction images. The MIP is the most reliable image for assessing motion artifacts: The right breast shows a “snow-peak” effect due to significant movement of the breast in the ventrodorsal direction during the early dynamic phase. Optimal, artifact-free presentation of the left breast. Fig. 6.10a, b Masking of DCIS by motion artifacts. a Subtraction slice image with linear, ribbonlike motion artifacts in the right breast (MRI artifact level II). Ideal imaging of the left breast. No obvious abnormalities in either breast. b Repeat examination with fewer motion artifacts (MRI artifact level I). Detection of now obvious, nonmasslike lesion in the central aspect of the right breast. Histology: DCIS.
Incorrect Positioning
Improper Administration of Contrast
 Typical reference points to check for correct contrast material administration (Fig. 6.5):
Typical reference points to check for correct contrast material administration (Fig. 6.5):
 Internal mammary arteries
Internal mammary arteries
 Nipples
Nipples
 Intramammary veins
Intramammary veins
Motion Artifacts
 The MIP presentation is the most reliable image to check for motion artifacts. Executed with excellent quality, it can be used to rule out artifacts caused by breast movements (Fig. 6.9).
The MIP presentation is the most reliable image to check for motion artifacts. Executed with excellent quality, it can be used to rule out artifacts caused by breast movements (Fig. 6.9).
Documentation and Classification
Artifacts and Sources of Error
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue

Full access? Get Clinical Tree