• Laparoscopic & prolonged gynecologic surgeries usually performed under GA
Laparoscopic procedures require complete relaxation of abdominal wall (ie, paralysis)
Std anesthesia techniques & precautions apply
Many laparoscopic procedures require prolonged Trendelenburg positioning for access to pelvis; in some pts, this may cause hemodynamic compromise, difficulty ventilating
• Transvaginal procedures & many abdominal procedures may be performed under neuraxial anesthesia/sedation, particularly if pt not candidate for GA due to medical comorbidities (though precludes use of paralytics)
Examples: Dilation & curettage/evacuation, operative hysteroscopy, vaginal hysterectomy or abdominal hysterectomy in pts not candidates for GA
• Both minilaparotomies & some laparoscopic procedures (most commonly sterilization) may be performed under sedation w/ local anesthesia only
PARENTERAL ANALGESIA IN OBSTETRICS
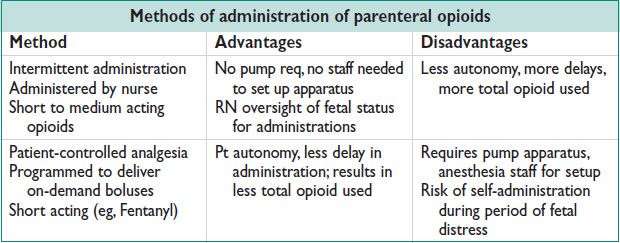
• All nonneuraxial methods provide only partial relief of labor pain.
May help laboring women cope w/ pain
Useful in cases of absolute contraindication to or pt refusal of neuraxial anesthesia
• Opioids act as opioid receptor agonists: Mu, kappa, delta
G-protein–coupled receptors → ↓ intracellular Ca → inhibition of release of pain neurotransmitters. Distributed through brain, terminal axons of spinal cord afferents
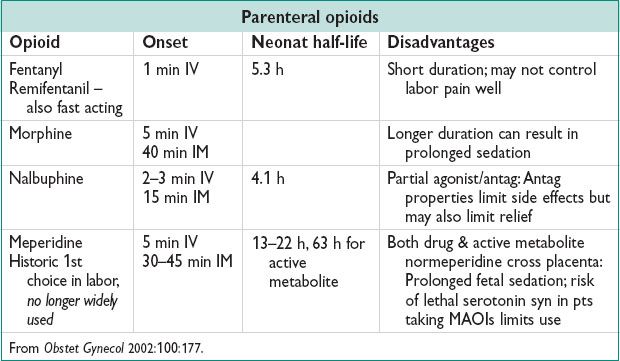
• Xfer across the placenta is rapid & signif; fetal effects may limit use
Drug xfer affected by prot binding capacity, size, ionization
In general, all local anesthetics & opioids transfuse freely across the placenta
Fetal acidosis results in ion trapping → fetal drug accum
• Side effects of systemic opioids
Maternal: Sedation, respiratory depression, N/V
Fetal: Decreased fetal HR variability during labor; pseudosinusoidal HR pattern, respiratory depression at birth. Use short-acting opioid w/ no active metabolites, if poss. Monit fetus continuously during administration of systemic opioids. Avoid administration shortly before deliv.
• Sedatives: Do not provide analgesia; typical use is for sleep/relaxation in latent labor
NEURAXIAL ANESTHESIA IN OBSTETRICS
• Most effective method for labor pain
• Also std for C/S, postpartum tubal ligations, urgent postpartum procedures whenever poss
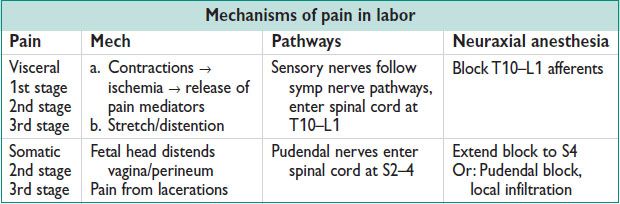
• Indications for spinal/epidural anesthesia in labor
Maternal request
Anticipation of operative vaginal deliv or shoulder dystocia; breech extraction; high risk of C/S; Risk of hemorrhage; difficult intubation
Maternal condition where signif pain or stress would create medical risk (eg, sev respiratory or cardiac dz)
Maternal condition which could worsen & potentially limit use of neuraxial anesthesia later in labor course (eg, worsening thrombocytopenia or coagulopathy)
• Contraindications to spinal/epidural anesthesia in labor
Absolute: Maternal refusal, uncooperative pt; soft tissue infxn of site; uncorrected hypovolemia; uncorrected therapeutic anticoagulation; Lovenox w/i 24 h; certain spinal conditions (eg, ependymoma); sev thrombocytopenia (<50 K)
Relative: Certain spinal conditions (eg, discectomy, rod fusion); mod thrombocytopenia (<75 K); LP shunt, some neurologic dzs (ie, multiple sclerosis); fixed cardiac output conditions (ie, AS)
• Types of neuraxial blocks: Spinal, epidural, & CSE
Spinal:
Anesthetic/opioid delivered directly into spinal fluid w/ needle through dural puncture
Benefits: Rapid onset (2 min); 1/20 epidural dose used so less risk tox
Disadvantages: Limited duration (1–1.5 h)
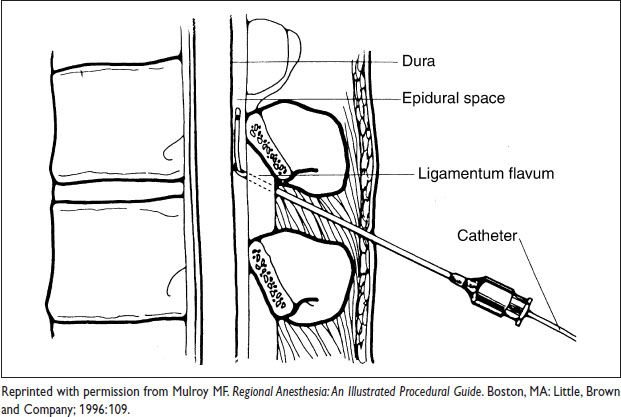
Epidural:
Anesthetic/opioid delivered into epidural space via continuous infusion through catheter
Benefits: Ability to continuously infuse & adjust dosage as needed; pt controlled
Disadvantages: Slower onset (20 min), larger doses used (20× spinal doses)
CSE:
Meds delivered directly into spinal fluid, then catheter placed in epidural space
Benefit: Combination of rapid onset & ability to continuously infuse
Disadvantages: More technically challenging than epidural or spinal alone; increased risk of PDPH compared to spinal alone
Figure 4.1 Epidural block