Chapter 4 ANEMIA
General Discussion
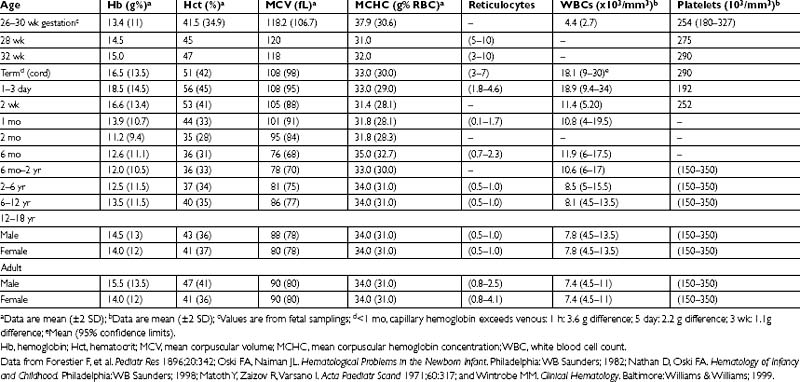
Anemia is a frequent laboratory abnormality in children, affecting as many as 20% of children in the United States and as many as 80% of children in developing countries. Anemia is defined as a decreased concentration of hemoglobin and red blood cell (RBC) mass compared with age-matched controls. Age-specific blood cell indices are outlined below in Table 4-1.
Medications Associated with Anemia
Acetylsalicylic acid (in patients with G6PD deficiency)
Antibacterials (in patients with G6PD deficiency)
Antimalarials (in patients with G6PD deficiency)
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) medications
Methylene blue (in patients with G6PD deficiency)
Phenacetin (in patients with G6PD deficiency)
Phenazopyridine (in patients with G6PD deficiency)
Probenacid (in patients with G6PD deficiency)
Vitamin K analogues (in patients with G6PD deficiency)