Cardiovascular Changes in Pregnancy
Blood Volume
• Plasma vol ↑ 45% from 6–32 w gest to 4700–5200 mL
• RBC mass ↑ by 20–30% (from ↑ production of RBCs)
• Plasma vol ↑ more than RBC vol, causing physiologic hemodilution → anemia ↑ erythrocyte 2,3-diphosphoglycerate conc, ↓ affinity of mat Hgb for O2 → facilitates dissociation of oxygen from Hgb → preferential xfer of O2 to fetus
Hemodynamic Profile
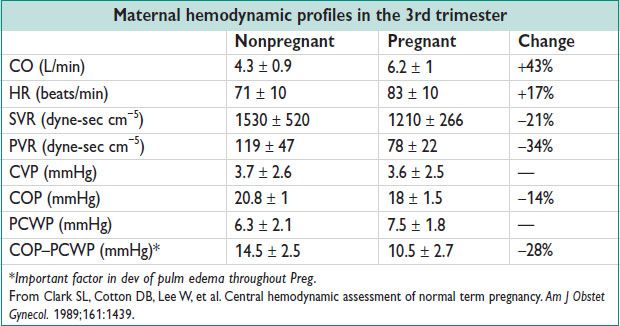
• CO ↑ 30–50% during Preg (50% of that during 1st 8 w)
Turning from supine to left lateral recumbent position → release of vena caval compression by gravid uterus can ↑ CO by 25–30%
• Uterine bld flow ↑ 10-fold to 500–800 mL/min (17% of total CO at term)
• Renal bld flow ↑ by 50%. No change in perfusion to brain or liver.
• ↑ HR at 5 w → max ↑ 15–20 beats/min by 32 w to term (Am J Physiol 1989;256:H1060)
• ↓ BP from 7 w to nadir 5–10 mmHg systolic & 10–15 mmHg diastolic by 24–32 w, then ↑ toward nonpregnant values at term (Am J Med 1980;68:97)
Heart Sounds (Am Heart J 1966;71:741)
• Benign systolic flow murmur develops in more than 95% of pregnant women: ↑ CO → turbulent flow over pulmonic or aortic valve
Audible 1st btw 12 & 20 w w/ regression usually by 1 w postpartum
Intrapartum Hemodynamic Changes
• 1st stage labor: 12–31% ↑ CO. 2nd stage: 49% ↑ CO. ≈2-fold ↑ from nonpregnant.
• Contractions cause 300–500 mL xfer of bld from uterus to general circulation
SBP & DBP ↑ by 35 & 25 mmHg respectively
Postpartum Hemodynamic Changes
• 60–80% ≠ CO w/i 10–15 min of vaginal deliv: Release of venocaval obst, autotransfusion of uteroplacental bld, rapid mobilization of extravascular fluid → watch for pulm edema. CO returns to prelabor value by 1-h postpartum.
• Important to monit women w/ CVD closely until at least 24 h after deliv
• CV measurements (SV, SVR, CO) take up to 24 w to return to prepregnancy values
ECG Changes in Pregnancy
• Majority of pregnant pts have a nml ECG (Eur Heart J 2011;32:3147)
• Change in heart position (rotated to left) → 15–20º L axis deviation; mimics LV hypertrophy
• Common ECG changes: Transient ST segment & T wave changes; Q wave & inv T wave in lead III; attenuated Q wave in lead AVF; inv T wave in leads V1, V2, & occ V3
• Premature beats & sustained tachyarrhythmia ↑ in Preg. Ventricular & atrial ectopy in up to 50–60% of pregnant women. Symptomatic exacerbation of paroxysmal SVT in Preg in 20–44% of cases. 15% of pregnant women w/ CHD develop arrhythmia. Most palps are benign, but warrant a Holter monit. Limited data on antiarrhythmic meds: Weigh mat risk against potential fetal teratogenicity.
CHRONIC HYPERTENSION (CHTN)
Definitions
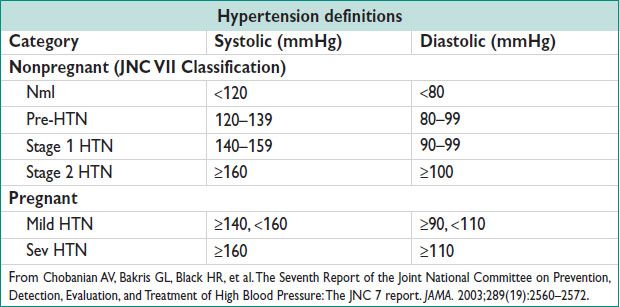
• CHTN in Preg: Use of antihypertensive medication prior to Preg, OR onset of HTN before Preg, prior to 20 w gest, or that persists beyond 12 w postpartum
Epidemiology and Etiology
• Nonpregnant: 10–15% Caucasian adults, 25% AA adults
• Pregnant: Occurs in up to 5% of pregnant women. Hypertensive disorders overall represent the most common medical complications of Preg (incid 6–8%)
• Essent (95%)
• Secondary:
Renal (4%): Renal artery stenosis, parenchymal
Endocrine (0.5%): Pheo, primary hyperaldo, Cushing’s
Coarct of the aorta (0.2%)
Other: Collagen vascular dz, sleep apnea
Workup
• H&P: Including fundoscopic, cardiac, abdominal, vascular, & neurologic exams
• Studies: Electrolytes, BUN/Cr, gluc, Hgb/Hct, UA, lipids, ECG
• W/u for secondary causes: Age <20 or >50, sudden onset, sev, refrac
• Additional w/u for Preg: Baseline HELLP labs including Hgb, Plt, Cr, AST/ALT, uric acid, 24-h urine prot
Complications
• Nonpregnant: Mostly long term, including TIA/CVA, CAD, CHF, CKI
↑ of 20 mmHg SBP or 10 mmHg DBP doubles CV complications (Lancet 2002;360:1903)
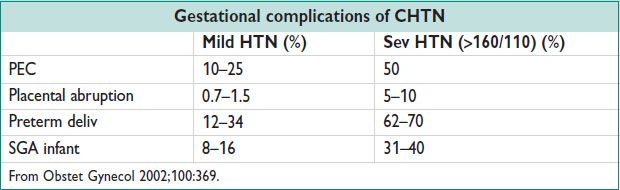
• Pregnant: Additional mat risks: Pulm edema, hypertensive encephalopathy, retinopathy, cerebral hemorrhage, acute renal failure
Additional fetal risks: Perinatal mortality ↑ 3–4×
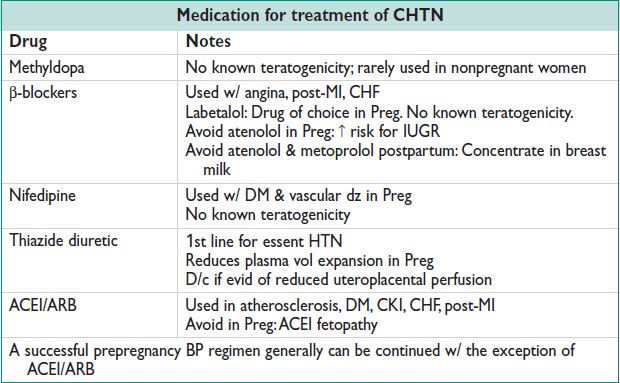
Rx goal: <140/90 mmHg (<130/80 mmHg w/ DM or renal dz) (NEJM 2003;348:610)
Additional Management in Pregnancy (Obstet Gynecol 2002;100:369)
• Lifestyle modifications preconception (each ↓ SBP by 5 mmHg)
Weight loss, diet (low saturated & total fat, low sodium), exercise, ↓ EtOH
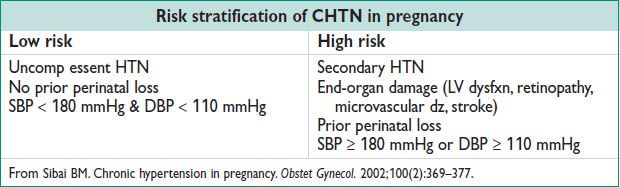
• Low risk: No antihypertensive drugs. US at 16–20 w, rpt at 28–30 w then monthly for growth assessment till term. Deliver at 38–39 w.
• High risk: Antihypertensive meds to keep BP <140/90 mmHg. US at 16–20 w, rpt at 28 w, then every 3–4 w until deliv. Serial fetal testing (NST, AFI) beginning at 28–32 w. Deliver at 39 w if BP controlled & no fetal growth restriction, otherwise deliver at 37–38 w.
HYPERTENSIVE CRISIS
Definition
• Hypertensive emergency: Elevated BP w/ target organ damage
• Hypertensive urgency: SBP > 210 or DBP > 120 w/ minimal or no target organ damage
Treatment
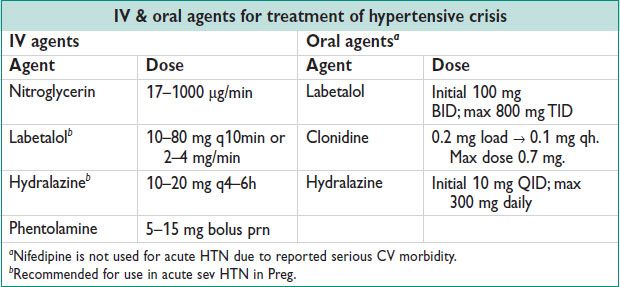
• Hypertensive emergency: ↓ MAP by 25% in minutes to 2 h using IV agents
• Hypertensive urgency: ↓ BP in hours using oral agents
PREGNANCY-RELATED HYPERTENSION
Definitions (And see chapter 11; For up to date details, Hypertension in Pregnancy, ACOG Task Force, 203)
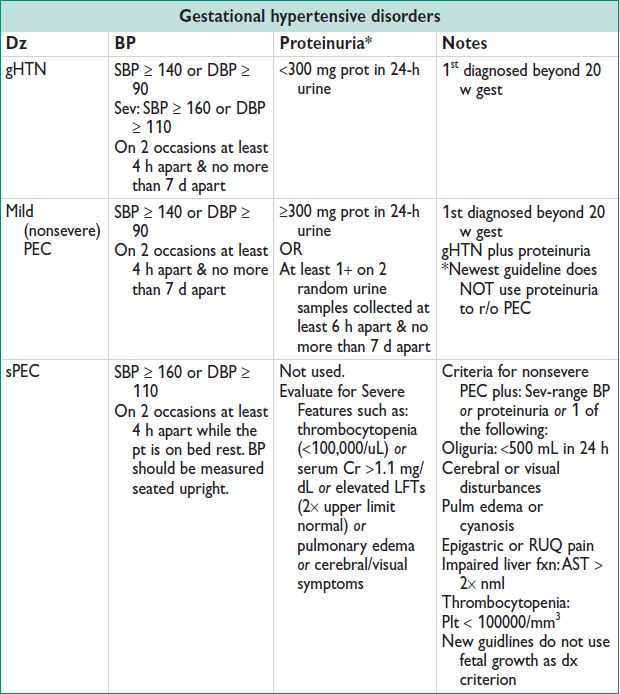
Epidemiology (Obstet Gynecol 2003;102:181)
• Risk factors for Preg-related HTN: Nulliparity, multifetal gest, obesity, AMA, prior PEC, CHTN, renal dz, DM, vascular & CTD, antiphospholipid Ab syn, AA race
• gHTN: 6–17% in nulliparous & 2–4% multiparous women
• PEC: 4–8% of all pregnancies; up to 18% in women w/ a h/o PEC
• Eclampsia: 1 in 2000–3448 pregnancies
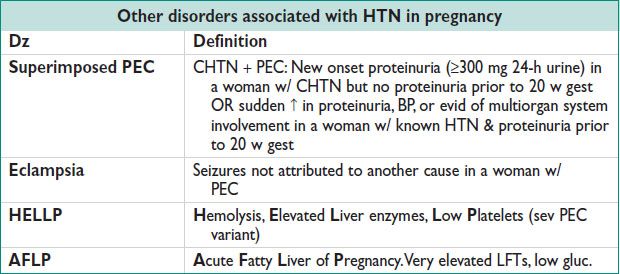
Etiology/Pathophysiology
• Poorly understood. Potential causes: Abn trophoblast invasion of uterine bld vessels, immunologic intolerance btw fetoplacental & mat tissues, maladaptation to the CV/inflamm changes of Preg, dietary deficiencies, genetic abnormalities (Obstet Gynecol 2003;102:181)
Prevention
• ≠ risk: H/o PEC, other hypertensive d/o, DM, abn uterine artery dopplers, nulliparity, multi gest → therefore, reduce risk factors early
• Low-dose ASA in mod- to high-risk pts (Obstet Gynecol 2010;116:402)
Prior PEC: Start ASA by 16 w: RR 0.47 (95% CI 0.34–0.65); NNT 9
Prior sPEC: Start ASA by 16 w: RR 0.09 (95% CI 0.02–0.37); NNT 7
Starting after 16 w → no benefit. Stop ASA ∼1 w prior to deliv.
Clinical Manifestations of PEC
• Cerebral: HA, dizziness, tinnitus
• Visual: Diplopia, scotomata, blurred-vision, amaurosis
• GI: Nausea, vomiting, epigastric/RUQ pain, hematemesis
• Renal: Oliguria, anuria, hematuria
Initial Workup
• Collect baseline bld work at 1st prenatal visit or at time of dz presentation
Hgb, Plt, Cr, AST/ALT, uric acid, 24-h urine prot. Rpt if ↑ clinical concern.
• Fetal eval: NST/AFI, growth US
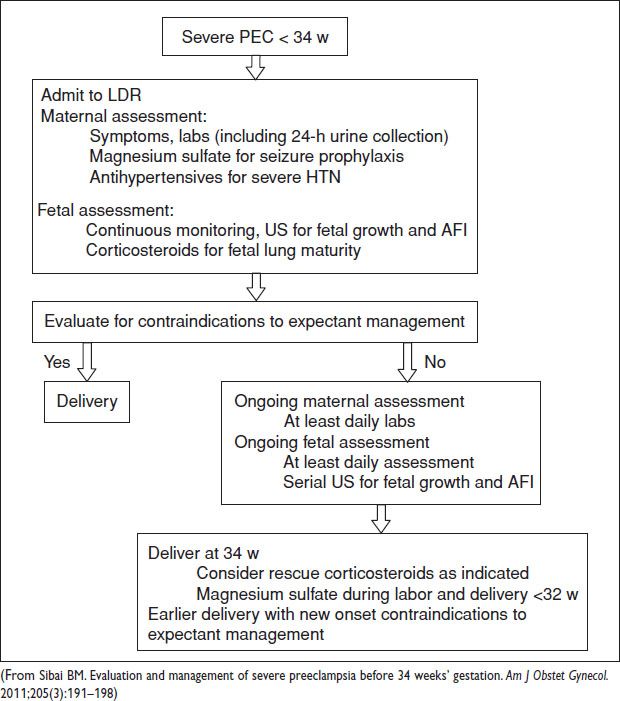
Management/Treatment
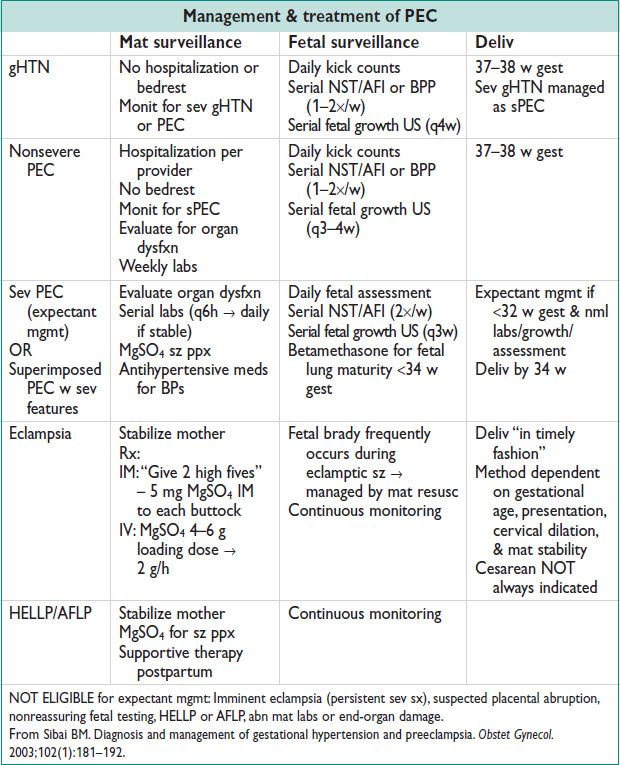
Figure 12.1 Algorithm for management of sPEC <34 weeks