CHAPTER 22 a collection of extravasated endometrial tissue. a condition occurring when active endometrial tissue invades the peritoneal cavity. human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) a substitute for luteinizing hormone used in fertility assistance to trigger ovulation. dilatation of the fallopian tube with fluid. an anomalous sac protruding from the ileum; caused by an incomplete closure of the yolk stalk. pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) inflammation within the fallopian tube. Pathology of the Fallopian Tubes • Infertility is suggested when conception does not occur within 1 year. • Caused by male or female reproductive abnormalities. • Most common cause of female infertility is ovulatory disorders. • Fibroids are responsible for 15% of infertility cases. • Other causes include oviduct disease, congenital uterine anomalies, endometrial pathology, cervical mucus abnormality, nutritional factors, metabolic disorders, and synechiae. • Medications are injected to stimulate follicular development. • Stimulates the pituitary gland to increase secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone. • Follicular growth is monitored by periodic ultrasound examinations. • Estradiol levels are monitored for timing of intramuscular injection of hCG.
Adnexal pathology and infertility
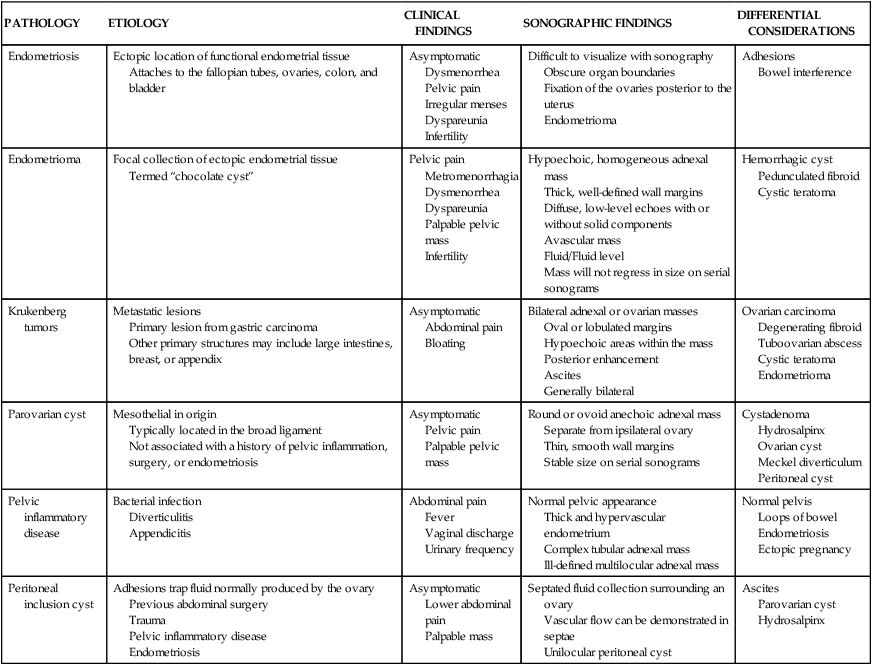
PATHOLOGY
ETIOLOGY
CLINICAL FINDINGS
SONOGRAPHIC FINDINGS
DIFFERENTIAL CONSIDERATIONS
Endometriosis
Ectopic location of functional endometrial tissue
Attaches to the fallopian tubes, ovaries, colon, and bladder
Asymptomatic
Dysmenorrhea
Pelvic pain
Irregular menses
Dyspareunia
Infertility
Difficult to visualize with sonography
Obscure organ boundaries
Fixation of the ovaries posterior to the uterus
Endometrioma
Adhesions
Bowel interference
Endometrioma
Focal collection of ectopic endometrial tissue
Termed “chocolate cyst”
Pelvic pain
Metromenorrhagia
Dysmenorrhea
Dyspareunia
Palpable pelvic mass
Infertility
Hypoechoic, homogeneous adnexal mass
Thick, well-defined wall margins
Diffuse, low-level echoes with or without solid components
Avascular mass
Fluid/Fluid level
Mass will not regress in size on serial sonograms
Hemorrhagic cyst
Pedunculated fibroid
Cystic teratoma
Krukenberg tumors
Metastatic lesions
Primary lesion from gastric carcinoma
Other primary structures may include large intestines, breast, or appendix
Asymptomatic
Abdominal pain
Bloating
Bilateral adnexal or ovarian masses
Oval or lobulated margins
Hypoechoic areas within the mass
Posterior enhancement
Ascites
Generally bilateral
Ovarian carcinoma
Degenerating fibroid
Tuboovarian abscess
Cystic teratoma
Endometrioma
Parovarian cyst
Mesothelial in origin
Typically located in the broad ligament
Not associated with a history of pelvic inflammation, surgery, or endometriosis
Asymptomatic
Pelvic pain
Palpable pelvic mass
Round or ovoid anechoic adnexal mass
Separate from ipsilateral ovary
Thin, smooth wall margins
Stable size on serial sonograms
Cystadenoma
Hydrosalpinx
Ovarian cyst
Meckel diverticulum
Peritoneal cyst
Pelvic inflammatory disease
Bacterial infection
Diverticulitis
Appendicitis
Abdominal pain
Fever
Vaginal discharge
Urinary frequency
Normal pelvic appearance
Thick and hypervascular endometrium
Complex tubular adnexal mass
Ill-defined multilocular adnexal mass
Normal pelvis
Loops of bowel
Endometriosis
Ectopic pregnancy
Peritoneal inclusion cyst
Adhesions trap fluid normally produced by the ovary
Previous abdominal surgery
Trauma
Pelvic inflammatory disease
Endometriosis
Asymptomatic
Lower abdominal pain
Palpable mass
Septated fluid collection surrounding an ovary
Vascular flow can be demonstrated in septae
Unilocular peritoneal cyst
Ascites
Parovarian cyst
Hydrosalpinx
PATHOLOGY
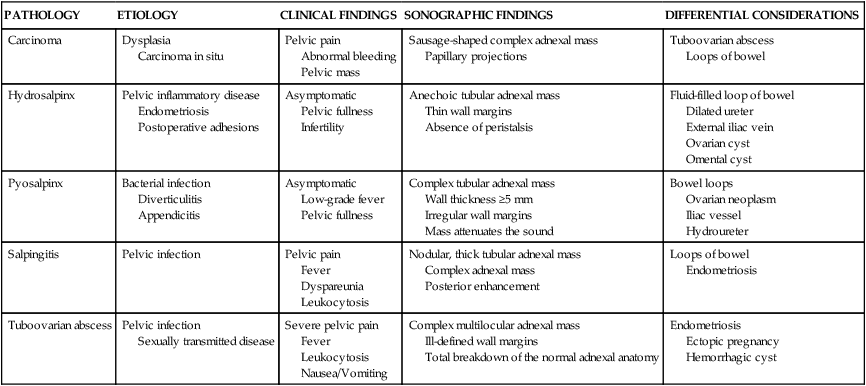
ETIOLOGY
CLINICAL FINDINGS
SONOGRAPHIC FINDINGS
DIFFERENTIAL CONSIDERATIONS
Carcinoma
Dysplasia
Carcinoma in situ
Pelvic pain
Abnormal bleeding
Pelvic mass
Sausage-shaped complex adnexal mass
Papillary projections
Tuboovarian abscess
Loops of bowel
Hydrosalpinx
Pelvic inflammatory disease
Endometriosis
Postoperative adhesions
Asymptomatic
Pelvic fullness
Infertility
Anechoic tubular adnexal mass
Thin wall margins
Absence of peristalsis
Fluid-filled loop of bowel
Dilated ureter
External iliac vein
Ovarian cyst
Omental cyst
Pyosalpinx
Bacterial infection
Diverticulitis
Appendicitis
Asymptomatic
Low-grade fever
Pelvic fullness
Complex tubular adnexal mass
Wall thickness ≥5 mm
Irregular wall margins
Mass attenuates the sound
Bowel loops
Ovarian neoplasm
Iliac vessel
Hydroureter
Salpingitis
Pelvic infection
Pelvic pain
Fever
Dyspareunia
Leukocytosis
Nodular, thick tubular adnexal mass
Complex adnexal mass
Posterior enhancement
Loops of bowel
Endometriosis
Tuboovarian abscess
Pelvic infection
Sexually transmitted disease
Severe pelvic pain
Fever
Leukocytosis
Nausea/Vomiting
Complex multilocular adnexal mass
Ill-defined wall margins
Total breakdown of the normal adnexal anatomy
Endometriosis
Ectopic pregnancy
Hemorrhagic cyst
Infertility
Methods of assisted reproductive technologies (ART)
Ovarian induction therapy
Adnexal pathology and infertility



